Exploring the Features and Compression Techniques of ZIP Files
RAR and ZIP are two widely used file archive formats, both offering distinct features and functionalities. While ZIP is known for its compatibility and accessibility, RAR is recognized for its superior compression capabilities. Understanding the differences between these two formats is crucial for efficiently managing and transferring data.
Briefly about ZIP Archive Format
ZIP is a widely used archive file format that allows the compression and storage of one or more files and folders into a single file. It employs lossless data compression techniques to reduce file size, making it easier to transfer and store data. ZIP files can be decompressed to retrieve the original files and folders, making them popular for file compression and sharing purposes. More details about the ZIP archive can be found at the link .
Briefly about RAR Archive Format
RAR is a proprietary archive file format that allows for data compression, error recovery, and file spanning. It is known for its efficient compression algorithms, making it suitable for compressing large files. RAR archives can be split into multiple volumes, making it easier to distribute them across different storage devices or transfer them over the internet. For more information about RAR, follow the link .
Detailing the compression algorithms and efficiency for Rar and Zip format.
RAR generally provides faster file compression and decompression, especially when working with large amounts of data. This is due to more efficient compression algorithms and the ability to manage large files, which allows for faster data processing. However, this may require more processing power than ZIP, which may impact performance when working with smaller files.
On the other hand, ZIP generally offers faster file archiving and unzipping speeds, especially when handling small to medium file sizes. Thanks to its simplicity and optimized algorithms, ZIP provides fast data processing, making it the preferred choice for general archiving and file compression needs.
For assessing the compression speed, identical files were selected based on their size and quantity. This data was then utilized to create a dependency diagram illustrating two compression types: normal and maximum. The measurement process was executed across various file categories, including textual, multimedia, and mixed files. Smaller values were deemed indicative of more favorable outcomes, according to the gathered data.
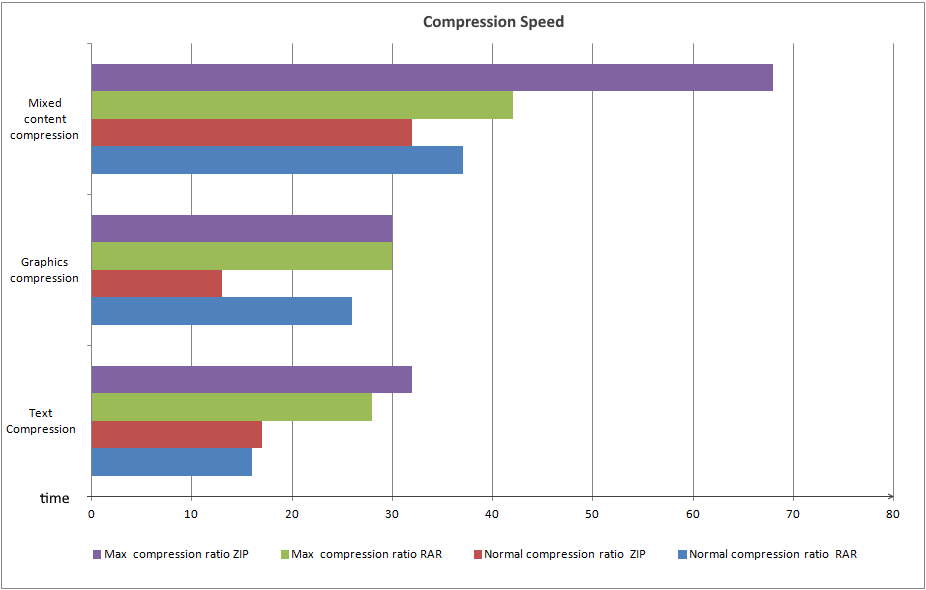
Comparing the time taken to extract mixed files
The extraction speed of ZIP archives has been commonly observed to be faster than that of RAR archives, as indicated by various performance tests and user experiences. This trend is often attributed to the different compression algorithms used in the two formats, with ZIP typically being more efficient in terms of extraction speed. However, it’s important to note that the extraction speed can vary depending on the software used, the size of the files, and the overall complexity of the compressed data. For specific cases or scenarios, the extraction speed may differ, but in general, ZIP archives tend to exhibit faster extraction rates compared to RAR archives. On the graph presented below, the lower the value, the better the decompression speed.
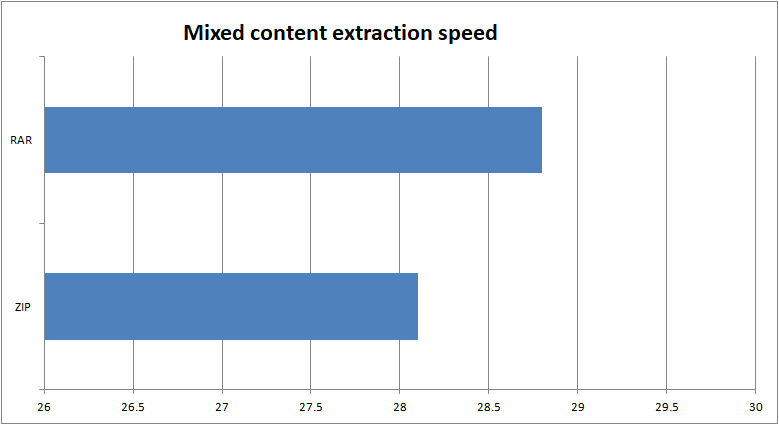
Comparing the time taken to extract mixed files
ZIP format is renowned for its widespread compatibility and user-friendly nature. It is a popular choice for general file compression and archiving, offering seamless integration across various platforms and operating systems. With its straightforward and accessible interface, ZIP allows users to compress and extract files effortlessly, making it an ideal option for everyday users and simple archiving tasks.ZIP format is ideally suited for situations where broad compatibility and straightforward archiving are essential, making it a preferred choice for general file compression, email attachments, and simple data archiving. Its widespread acceptance across multiple platforms and user-friendly interface make it an excellent option for everyday file management needs.
On the other hand, RAR format stands out for its advanced features and exceptional compression capabilities. It is designed to handle larger files and complex archiving requirements effectively. RAR offers a higher compression ratio compared to ZIP, ensuring that files are reduced to a smaller size without compromising on quality. Additionally, RAR provides encryption options and the ability to create self-extracting archives, making it an excellent choice for users seeking enhanced security and advanced archiving functionalities.
RAR format is best employed for scenarios where high compression efficiency and advanced archiving capabilities are paramount. It is particularly valuable for compressing large files or folders, as well as data that needs to be securely encrypted. Its ability to create self-extracting archives and handle complex archiving tasks makes it a valuable tool for users dealing with extensive data sets and sensitive information.
Summary of Key Differences
At the end, the primary distinction between ZIP and RAR formats lies in their compression efficiency, functionality, and intended usage. While ZIP is widely adopted for its simplicity and compatibility across various platforms, RAR stands out with its superior compression rates and encryption capabilities, making it a preferred choice for handling large files and sensitive data. Understanding these differences can assist users in selecting the most suitable format based on their unique requirements, balancing factors such as file size, security needs, and intended application.
People have been asking
1. Is RAR or ZIP smaller?
The compressed size of RAR or ZIP files varies depending on factors such as the type of data, compression level, and file size. Generally, both formats utilize different compression algorithms, resulting in varying file sizes under different conditions.
2. Does RAR reduce quality?
RAR is primarily designed for data compression and archiving, and it does not alter the quality of files during the compression process. The lossless compression algorithms of RAR help in reducing file size without compromising the original quality of the content.
3. Which is more resilient to file corruption, ZIP or RAR?
RAR files are known for their robust error recovery capabilities, making them more resilient to corruption compared to ZIP files. While both formats offer some level of protection against corruption, RAR archives are generally more reliable and less prone to data loss.