LHA File Format
Key Features of LHA Archives - How to Open, Compress, Extract, and Manage LHA Archives
LHA Archive Format
LHA, an archive format developed for efficient data compression and software distribution, was particularly popular in the 1990s when storage space was at a premium. Utilizing the Lempel-Ziv-Huffman (LZH) compression algorithm, LHA was commonly used to compress software files on DOS and early Windows platforms, providing efficient compression and the ability to archive multiple files into a single archive .
General LHA Archive Information
LHA archives use the LZH compression algorithm, a combination of Lempel-Ziv encoding and Huffman coding. This provides a good balance between compression efficiency and speed. The .lha extension is the most common identifier for files compressed in this format. Although its popularity has waned with the advent of modern compression methods like ZIP and RAR, LHA remains significant in retro computing, Japanese software distribution, and preservation of older archives.
LHA Archives History
- 1988: LHA was initially released by Haruyasu Yoshizaki under the name LHarc. It introduced LZH compression, which combined Lempel-Ziv encoding with Huffman coding.
- Early 1990s: LHA became widely used for software distribution, particularly for games and shareware on DOS and early Windows platforms.
- Mid-1990s: As internet usage increased, formats like ZIP gained dominance, but LHA remained a preferred choice in specific regions, such as Japan.
- 2000s: Modern compression formats like RAR and 7z surpassed LHA in popularity due to their advanced features and better compression ratios.
- Today: LHA is still in use for retro computing and archival purposes, particularly in the preservation of older software and data.
Characteristics of LHA Archive
The LHA archive format emphasizes a balance between efficient compression and ease of use. Key characteristics include:
- Multi-file Archiving: Supports compressing multiple files and directories into a single
.lhaarchive. - LZH Algorithm: Utilizes the Lempel-Ziv-Huffman compression method.
- Metadata Support: Stores file metadata, such as names, timestamps, and attributes, within the archive.
- Cross-platform Compatibility: LHA archives can be used across various platforms with appropriate tools.
LHA Archives Compression Methods
The LHA archive format employs the LZH compression algorithm, which combines:
- Lempel-Ziv Encoding: Identifies repetitive data patterns to achieve efficient compression.
- Huffman Coding: Optimizes the encoding of data by replacing frequent patterns with shorter codes.
- Checksum Verification: Ensures data integrity by including checksums within the archive.
- Optional Enhancements: Certain implementations of LHA may incorporate additional features like encryption or self-extracting archives.
.lha Supported Operations
Aspose.Zip provides robust support for handling .lha archives:
- Full Extraction: Extract all files from an
.lhaarchive while maintaining original structure and metadata. - Selective Extraction: Decompress specific files or folders within an
.lhaarchive.
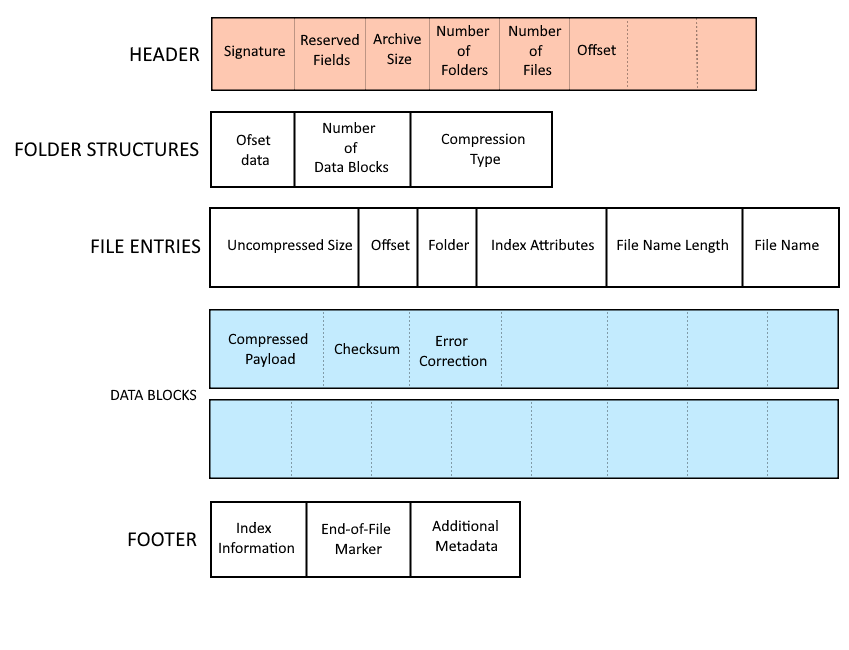
Structure of .LHA File
The structure of an LHA file is straightforward yet versatile:
- Header:
- Archive name and version.
- Compression method identifier.
- File metadata, including name, timestamp, and attributes.
- Compressed Data:
- The main payload compressed using the LZH algorithm.
- Footer:
- Optional checksum or data integrity information.
Popularity of the LHA Format
The LHA format was particularly popular in the 1990s for distributing software and games. Although largely replaced by modern compression formats, it retains a niche following, especially in Japan and among retro computing enthusiasts. LHA’s simplicity and support for metadata have ensured its continued relevance in specific contexts.
Examples of Using LHA Archives
This section provides code examples demonstrating how to compress and open LHA archives using C#, Java, and Python.NET. These examples utilize libraries like Aspose.Zip for handling LHA files and highlight practical uses in modern development.
The first code-snippet opens an LHA archive (subdir.lzh) and extracts all its contents into a specified folder called extracted. It unpacks the entire archive, including all files and folders, preserving their structure. The second example opens an LHA archive (sample.lzh) and extracts only the first file in the archive (Entries[0]) to a specified output stream (destinationStream), allowing for selective extraction of files.
Unpacking the LHA file into a folder via C#
using (LhaArchive a = new LhaArchive(File.OpenRead("subdir.lzh")))
{
a.ExtractToDirectory("extracted");
}
Extracting a single file from an LHA archive via C#
using (LhaArchive a = new LhaArchive("sample.lzh"))
{
a.Entries[0].Extract(destinationStream);
}
Additional Information
People have been asking
1. What operating systems support LHA archives?
LHA archives can be opened on multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, using tools like WinRAR, 7-Zip, and command-line utilities.
2. Why was LHA so popular in Japan?
LHA’s efficient compression and multi-file archiving capabilities made it ideal for distributing Japanese software and games during the 1990s, a time when file size constraints were critical.
3. Is LHA still relevant today?
While modern formats like ZIP and 7z have largely replaced LHA, it remains significant for retro computing, archival purposes, and certain niche applications.